Energy Conservation and Energy Efficiency are interchangeable words, Right?? But it is not. People often confuse Energy Efficiency and Energy Conservation. Energy Efficiency uses new technology to produce the same result, but the end goal is to use less energy to produce the same result. Energy conservation is a learned behavior that results in less energy use. Turning off the fans when you leave the room means you’re using the principles of Energy Conservation. Using LED Light Bulbs to produce the same amount of light as a regular light bulb is energy-efficient. Energy conservation is a new concept in the American Lingo, and it means to conserve or use less energy.
Here are 19 of the most efficient tips that help in Energy Conservation for a residential home. I have tried some of the tips in my house, and a few of my colleagues have tried a few outers. Almost all I recommended in the list below are a good fit for any residential home.
I’ve been in residential solar space for ten years and have a deep electrical engineering background. Armed with that knowledge, I’ve researched energy conservation topics and can simplify technical knowledge into something more understandable and readable. Thus, it makes complete sense to the layman who will help them with their Energy conservation plans and help save money on their utility bills.
Here is the list of 19 energy conservation I’ve learned and applied in my home.
- Energy Conservation – Introduction
- Phantom Load
- Insulation
- Time Base Electricity Rates
- Use dimmer switches or timers on lights.
- LED Bulbs or Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs
- Update Appliances to Energy Star Products
- Turning down the Manual Thermostat
- Programmable Thermostat
- Weather Stripping
- Insulating Window Treatment
- Heat pumps
- Insulating Blanket For Water Heater
- Reduce Dryer Usage
- Tune up your heating and cooling (HVAC) system
- Use Task Lighting
- Landscaping
- Green Roofs
- Switch to Solar Power
- Passive Solar Heating and Cooling
Some of the tips I’ve recommended below may not apply to specific regions, as they may have to do with weather conditions or utility providers. Please check with your utility regarding solar power, heat pumps, programmable thermostats, and time-based electricity.
Energy Conservation – Introduction
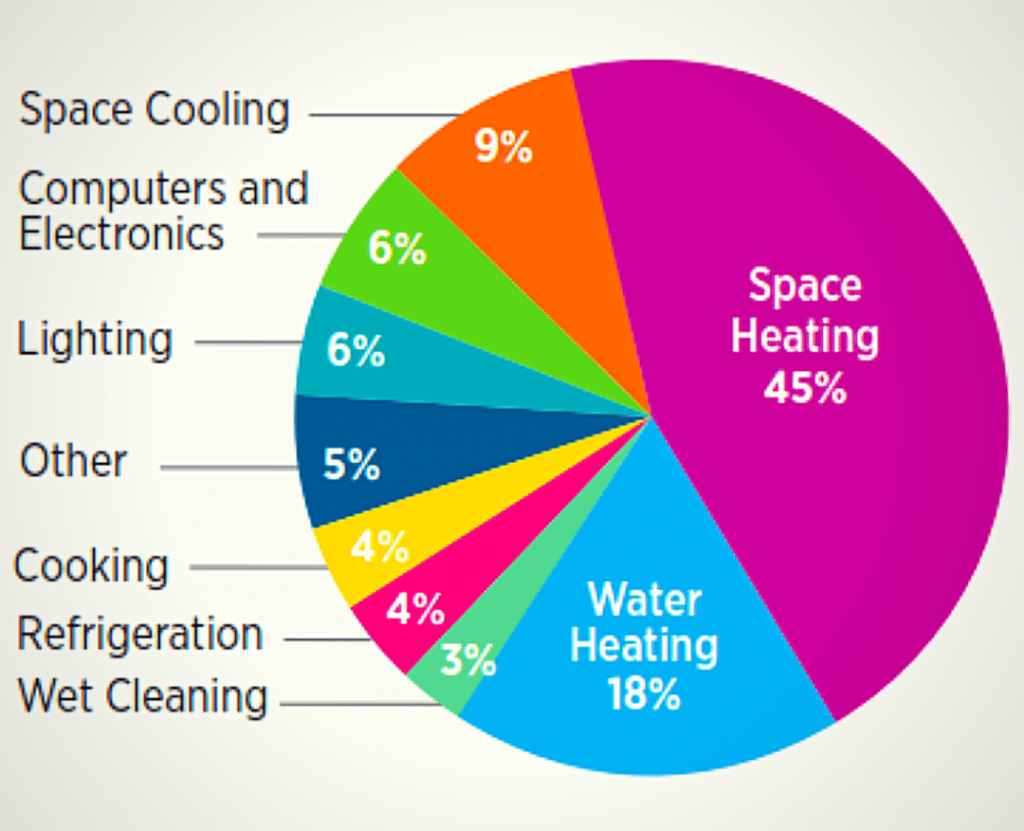
Ensuring your home is as energy efficient as possible helps ensure that your solar panels generate the maximum benefit for you. The analogy is like pouring water into a bucket with a giant hole at the bottom. You want to ensure your home doesn’t have a giant energy hole sucking away the benefits you’re getting from solar. As can be seen, the most significant energy usage lies in heating, and many of our tips have to do with keeping the heat in.
1. Phantom Load
Phantom Loads are electricity loads produced by your electrical appliances when they are in standby and idle mode. They are otherwise known as Vampire Loads. Most of these loads are generally small and have negligible cost on your usage. But when you start adding up energy usage from various appliances, they can significantly impact your usage. One recommended method is turning off all lights at night and looking for any LEDs indicating phantom load. You can reduce your Phantom Load by the following.
· Unplug the electrical appliances that are not in use in general,
· Use KillaWatt to monitor phantom loads and detect their usage.
· Use Energy Star Appliances when replacing your existing appliances. One, because they use power efficiently, and second, they use less power in standby mode.
2. Insulation
The insulation you can buy from any home improvement store

The Department of Energy estimates that a properly insulated attic can reduce your heating and cooling bills by 10 to 50 percent. It keeps your house temperatures in check in summer and works the opposite way for warm climates. In summer, it helps to stabilize your house’s indoor temps to keep cooling needs in check, and in winter, it’s the other way around. Insulation comes in 4 types Rolls and batts, loose-fill, rigid foam, and foam in place.
· Rolls and batts or blanket insulation are made from fiberglass and mineral wool and come in different sizes. Batts are blanket insulation pre-cut to manageable sizes: 15-24 inches wide by 48 or 93 inches long. Rolls are strips of insulation similar in width to rolls but much longer (25, 32, or 48 feet, for example).
· Loose Fill Insulation – They are usually made of cellulose or fiberglass in tiny pieces and are also known as blown-in insulation. That’s because it’s blown into the attic spaces using special pneumatic equipment. Fibers are blown into tight corners and fill spaces like odd-sized building cavities and attics with wires, ducts, and pipes.
· Rigid foam insulation – This type of insulation used on walls, roofs, and foundations is suitable for retrofits and new construction. All foam insulation products are petroleum-derived. The rigid foam insulation is more robust and does not shift out of place after installation. It is used in crawlspaces and basements because of its resistance to water and pests. It can also serve as an air barrier if the boards are adequately sealed along the edges and joints. Another benefit of it is its versatility. Expanded polystyrene (EPS), Extruded polystyrene (XPS), and Polyisocyanurate (polyiso) are examples of Rigid foam.
3. Time Base Electricity Rates
Utilities have encouraged customers to use electricity during off-peak hours to reduce their peak power demands. E.g., running your dishwasher during evening hours or using your dishwasher during odd hours. The exact hours and the premium you pay for electricity will be based on the utility company. Broadly speaking, peak hours start sometime in the afternoon and go into dusk. That is when people return home after a day of work and use more lights and appliances. These rates vary from utility, so it’s ideal to speak to customer service to ask them specifically if these rates are available and applicable. These programs are designed to pass on the savings to you through customer rebates or discounts on electricity rates.
4. Use dimmer switches or timers on lights.
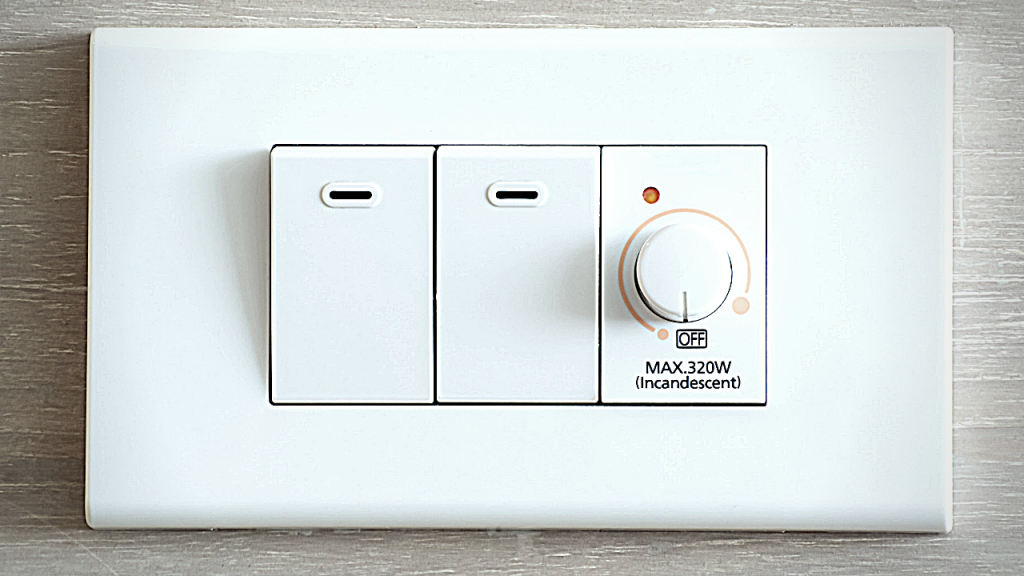

Dimmers are devices attached as part of your light switches. Dimmers adjust the brightness levels and vary the room’s lighting moods. This helps save energy by reducing the flow of electricity to the bulb, which allows the lights to operate at lower power outputs. As a result, the light output generated by the bulb is under less duress, hence extending the life of your light bulbs. Savings: 7‐10 percent of lighting costs. (EM)
5. LED Bulbs or Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs
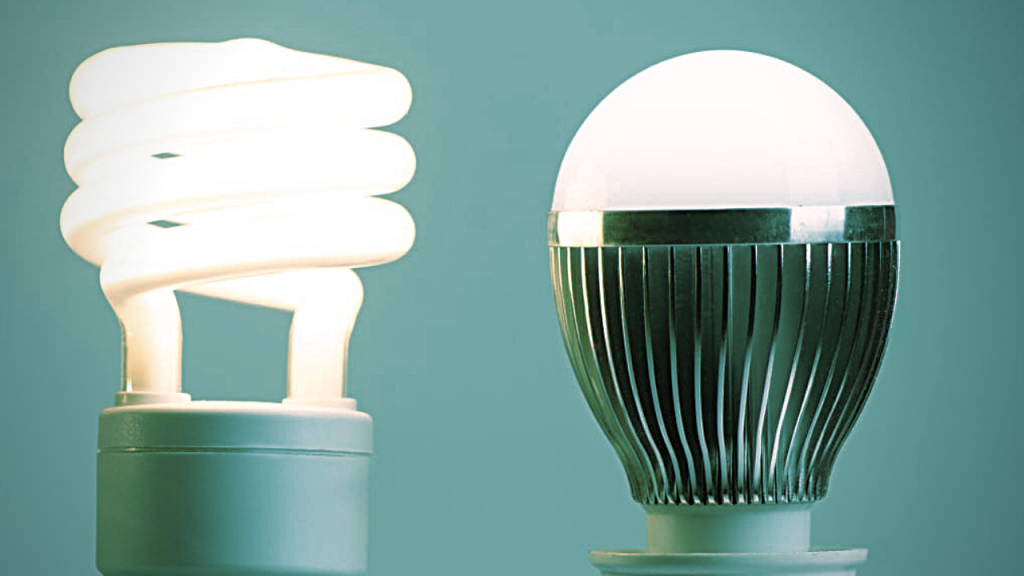

Incandescent light bulbs are being phased out, and the US wouldn’t be manufacturing any such light bulbs after 2025. Fluorescent bulbs last four to 10 times longer than regular light bulbs. Another option is going with the more expensive but even longer-lasting LED bulb. You might prefer the LED bulbs if you enjoy a directional light for reading, cooking, or working at home. CFL might be best for general home lighting, such as illuminating a room. [1]
6. Update Appliances to Energy Star Products
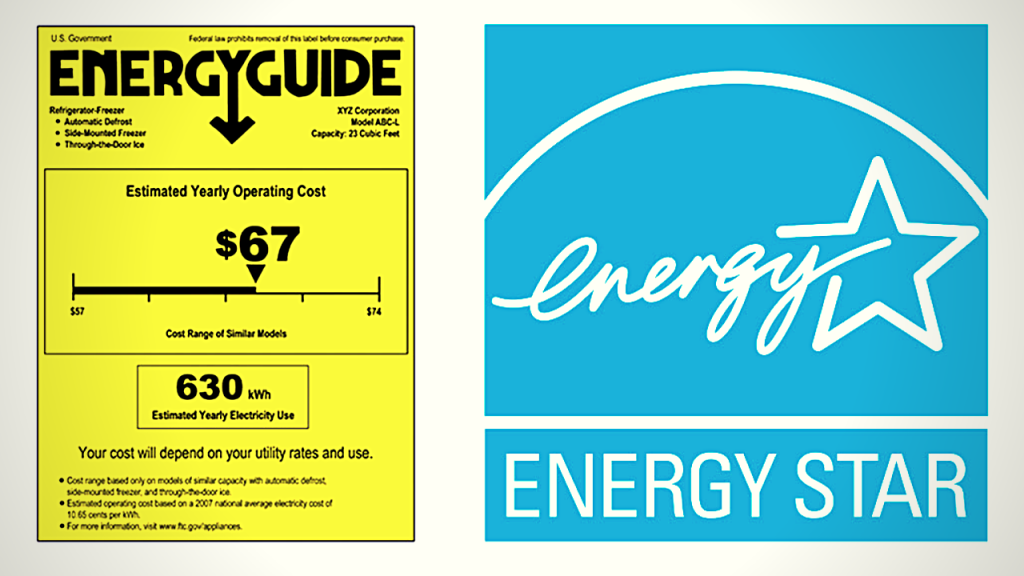
When shopping for appliances, realize that there are two price tags. The first is the purchase price, while the second is the cost of operating the appliance during its lifetime. Energy Star-rated appliances, including refrigerators, dishwashers, washers, dryers, TV are much more energy-efficient than models that meet the minimum federal standards for energy efficiency. For instance, Energy Star refrigerators are 20% more efficient than non-qualified models. Fridges with freezers on top use 10 – 25% less energy than side or bottom-mounted units. Energy Star dishwashers use less than 5.8 gallons of water per cycle, while older models before 1994 can use as much as 10 gallons per cycle.
7. Turning down the Manual Thermostat

One of the easiest ways to reduce electricity usage is by turning your thermostat to 78 degrees F during summer or lowering your 62 degrees F during winter. You will see instant savings in your electricity usage if you follow that principle. Also, read more about our programmable thermostat as an option if you’ve one or plan to buy one.
8. Programmable Thermostat
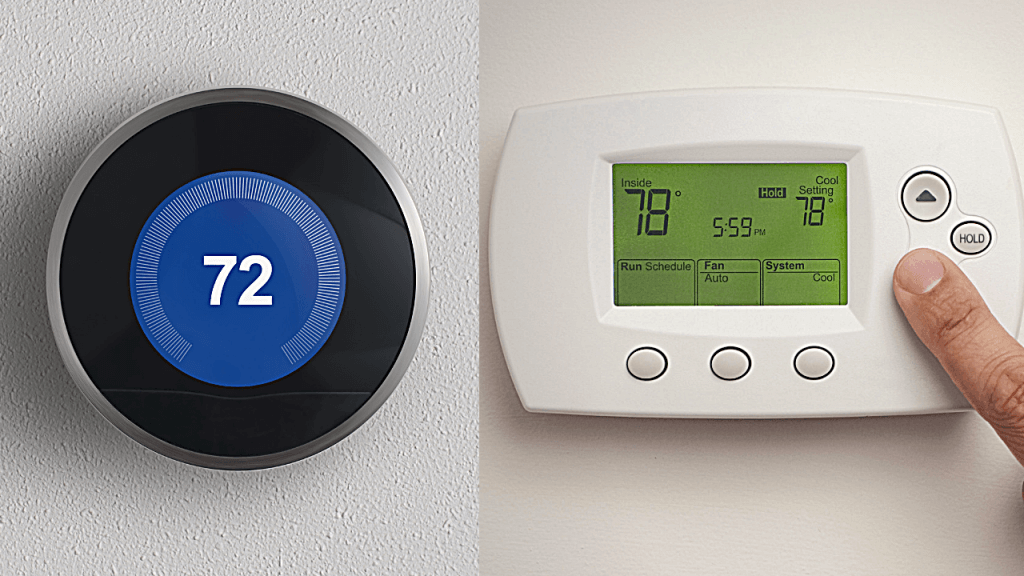
Programmable thermostats have become popular due to their energy- and money-saving benefits. A Programmable Thermostat can adjust the home heating and cooling schedule based on a pre-set schedule. This device can save users up to 10% on their home heating and Cooling cost per year when used. And it’s generally more accurate than a regular thermostat, according to the Department of Energy website, Energy.gov.
9. Weather Stripping
You might be surprised to see how much money you could save by patching your windows and doors. According to Energy Star, air leaks account for 30 to 40 percent of heating and cooling loss in homes that haven’t been weather-stripped. Patching down those doors and windows will save you money, around 10-15 %, on your electricity bills while keeping you warm. There might be a few options out there in the market that might help you in the short term. [2]
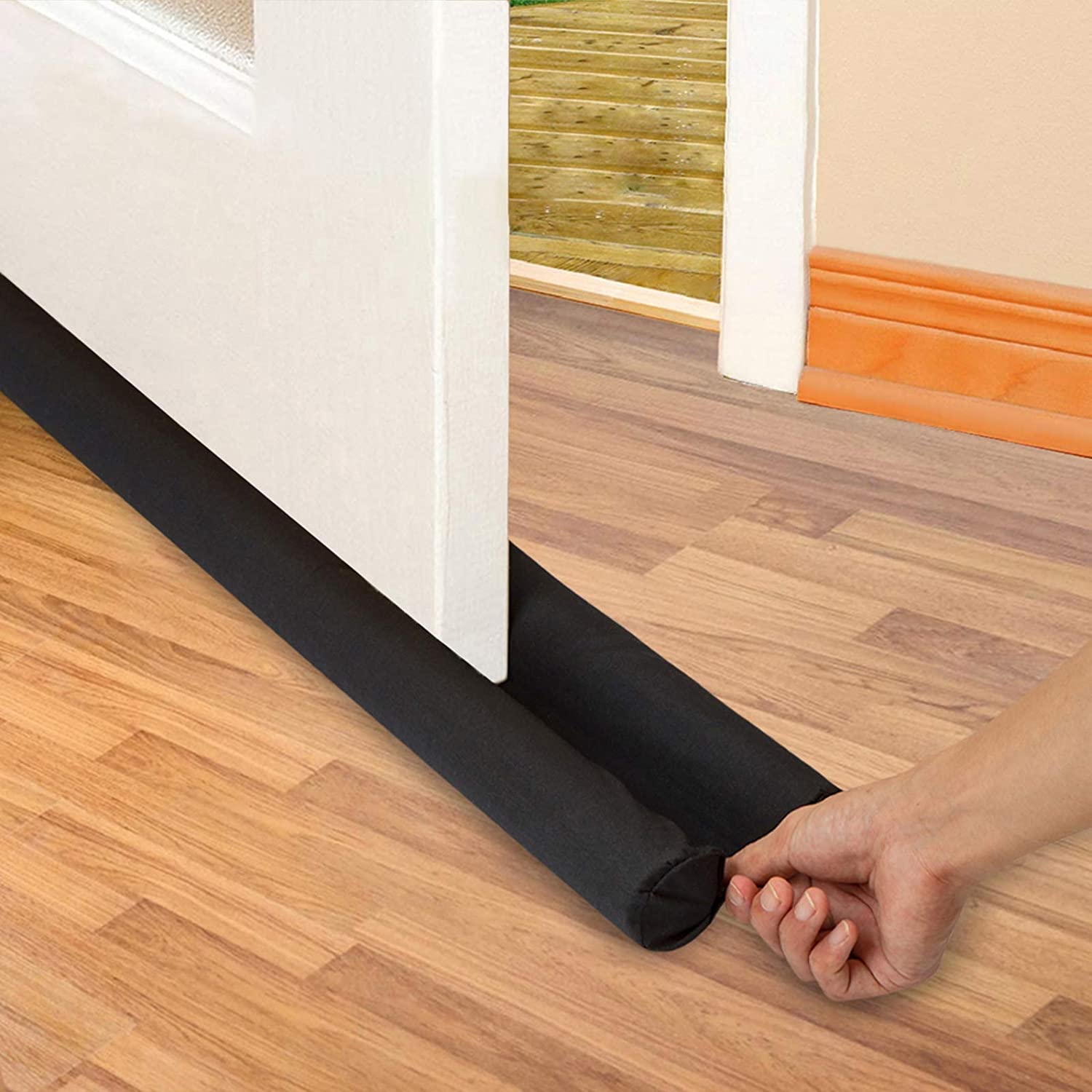

Door Sweeps are made of flat pieces of plastic, aluminum, or stainless steel with a strip of plastic or vinyl. The door sweep goes underneath a door to fill the space between the door and the ground.
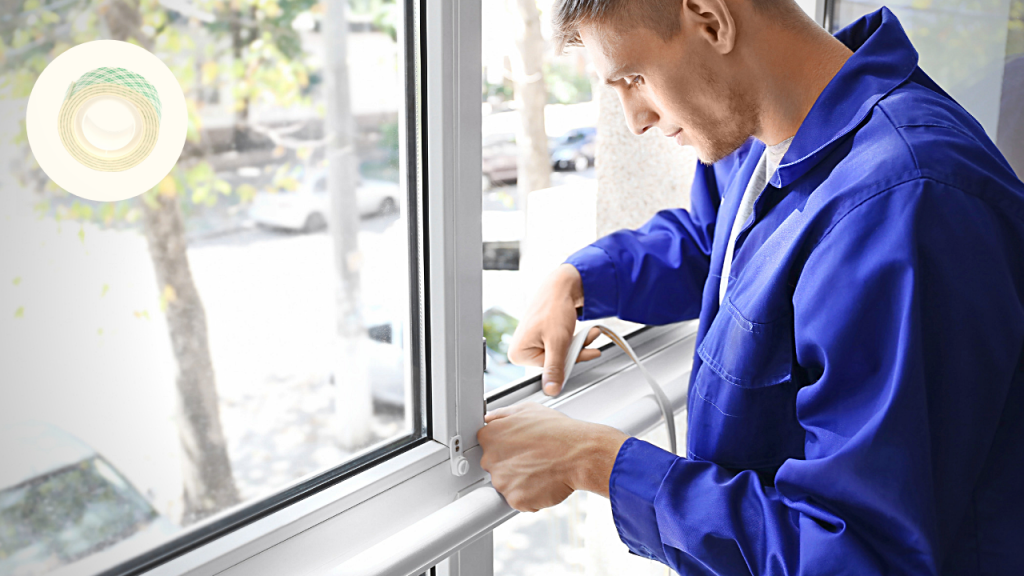

Foam tapes are one of the most accessible weather stripping and the least expensive weather-stripping tool. It’s an adhesive-based foam tape available in both rubber and plastic. When used, the foam tape is compressed by a door or a window, effectively sealing the air out. This is not a permanent solution and typically lasts 1 to 3 years.
10. Insulating Window Treatment
There are several options when it comes to Window Treatment
· Honey Comb Shade
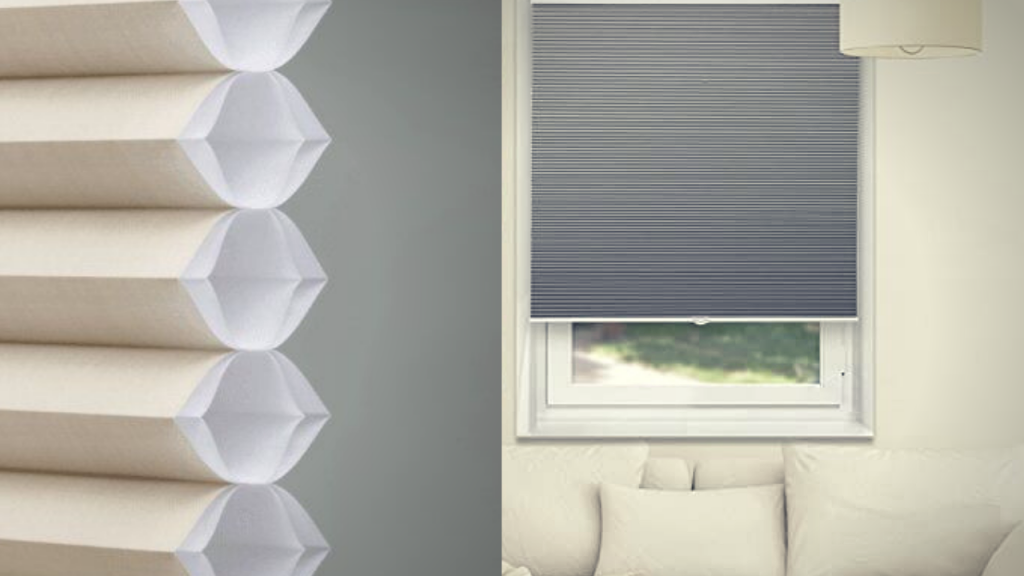

Cellular or honeycomb shades help reduce heat loss (up to 86%) and heat gain (up to 80%) together. Cellular shades have a honeycombed-shaped cell structure that can trap air within their pockets. And as a result, they provide a good level of insulation to the house. To get the best results while using Cellular shades, it’s best to use shades with two cells rather than one. These shades generally have the highest efficiency value when it comes to window treatments.
· Solar Shades
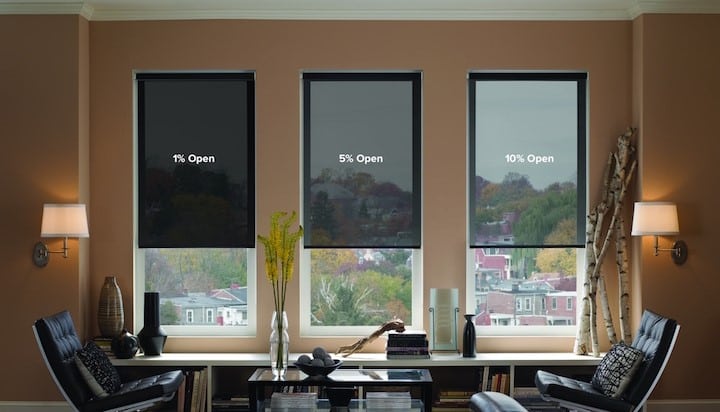

If you ever want to look outside, enjoy the view, and have insulating window treatments, then look no further than the Solar Shades. Solar Shades are a window treatment that will be a barrier between your home and harmful UV rays. This acts as an opaque material that will also allow you to have an outside view. Solar Shades come in various transparencies, which include a blackout option. The blackout option in solar shades blocks the sun from your room and will be completely dark during the day.
11. Heat pumps
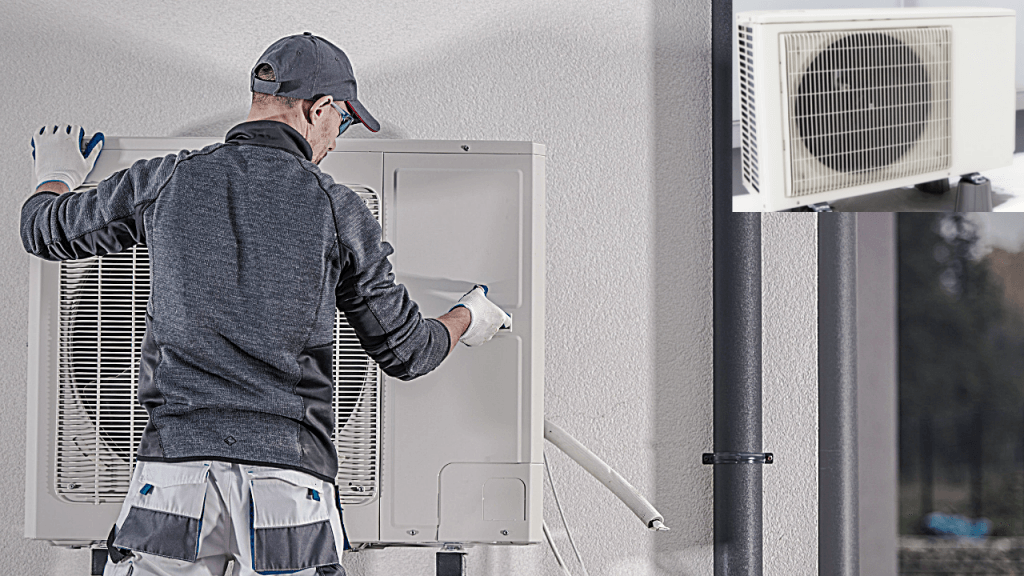

Heat pumps are the way to go for temperate climates requiring minimal to average heating and cooling needs. It offers an energy-efficient way compared to furnaces and air conditioners. The heat pumps in your refrigerator follow the same principle. The heat pump uses electricity to move heat from a perfect space to a warm space, making the space more relaxed and warm. During the warmers season, heat pumps move heat from your fantastic house into the warm outdoors and vice versa. This movement of heat is called heat transfer and is also called space conditioning. The cost of operating is one-quarter of the conventional heating or cooling appliances. There are three types of heat pumps: air-to-air, water source, and geothermal. The most uncommon version is the geothermal heat pump, where heat is transferred to your house from the ground or a nearby water source.
The heat pump can reduce your electricity usage for heating by 30%-40% compared to furnaces and baseboard heaters.
12. Insulating Blanket For Water Heater
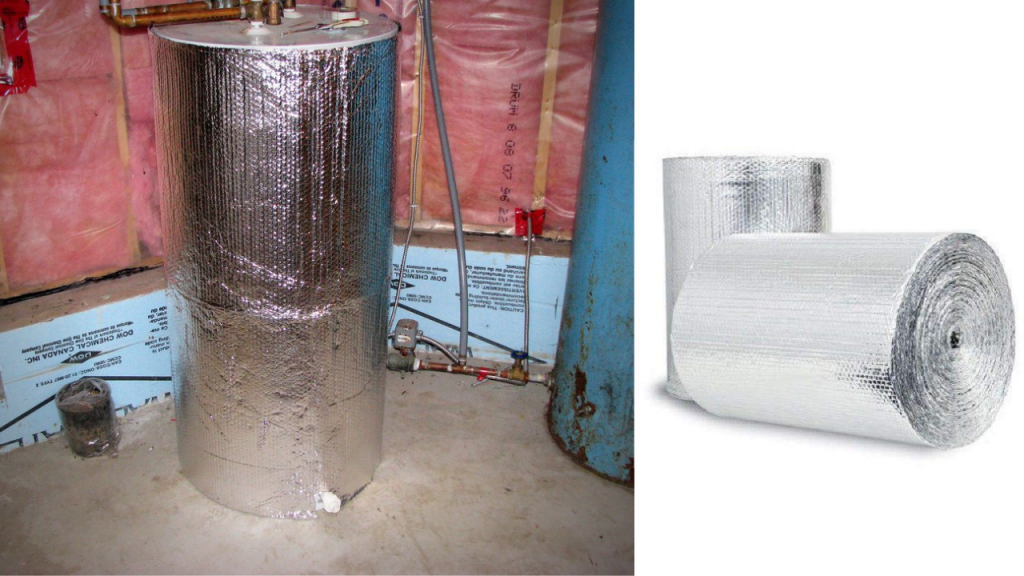

An electric water heater uses a significant amount of electricity compared to every other appliance. An insulation blanket or water heater blanket is a blanket that wraps around your water heater from it losing heat. As a result, it also helps the hot water to maintain a consistent temperature. An Insulation blanket is typically made of foil to denim, depending on how much insulation you would need for your water heater.
The US Department of Energy states that homeowners could save between $150-$200 annually by installing a water blanket. [3] That translates to between 7-16% of your annual bill. Insulation blankets are made of various materials—from foil and fiberglass to denim. It depends on how much insulation your water heater needs. They are rated on their R-value, which measures thermal resistance. The higher the R-value, the more insulation it will provide. You can find pre-cut jackets or blankets available for around $20.
13. Reduce Dryer Usage
Don’t over‐dry clothes. The dryer uses an average of 3000W of power, and if you’re going to over-dry your clothes, you will be using excess electricity. As a result, it will increase energy use, and your clothes will probably shrink and generate static electricity. This eventually shortens fabric life. After each use, its cleaning the dryer filter is necessary because a clogged filter will reduce airflow and dryer performance. Check out other Energy Saving Tips When it comes to good housekeeping.
14. Tune up your heating and cooling (HVAC) system

An HVAC system is an essential part of any building or house. There are a couple of reasons why you would want to tune it up regularly. One to make sure it works, and the other helps keep your energy bills down.
· Plug Air Seals
One of the easiest ways to do that is to make sure you plug your seals into the air duct system. This way, you can prevent the air from escaping before it gets inside your home.
· Preserve Air Flow
The other way you can do that is to preserve the airflow by keeping the HVAC unit free from dust and debris. Dust and debris can clog the system and force the HVAC system to work harder.
· Cleaning Air Filters
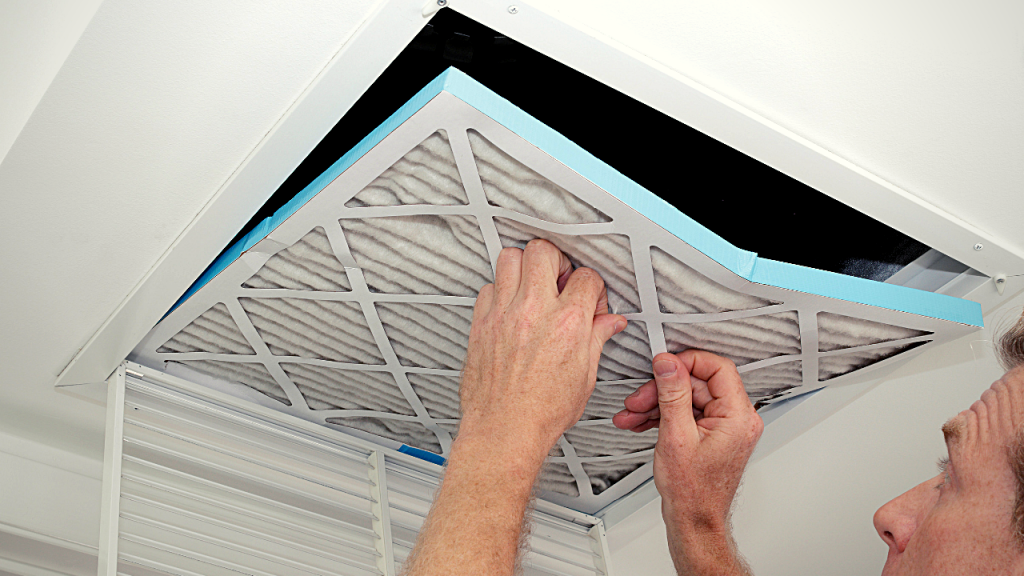

As the HVAC system operates regularly, the air filter gets clogged with dirt, dust, and debris. It’s important to note that it’s a sign of a sound working HVAC system. On the flip side, it requires regular cleaning because the dirtier the filter, the more complex the HVAC system needs to work. This will increase your energy use and your electricity bills.
15. Use Task Lighting

Task lighting is lighting up the area you work in instead of the entire room and, for example, using under cabinet lighting for kitchen sinks and countertops and using Lamps to light the room, rather than turning on the entire light in the room. This usage helps to reduce your electricity usage costs in the long term.
16. Landscaping

Landscaping or putting in trees or shrubs can make your home look pretty and beautiful. A strategically placed tree or shrub can cool your house in summer and reduce energy bills. The tree or vine can provide adequate shade, act as a windbreak, and reduce your energy bill. Based on a study, a well-positioned tree or trees can reduce the nearby summertime temperature by 3-5 degrees.
17. Green Roofs
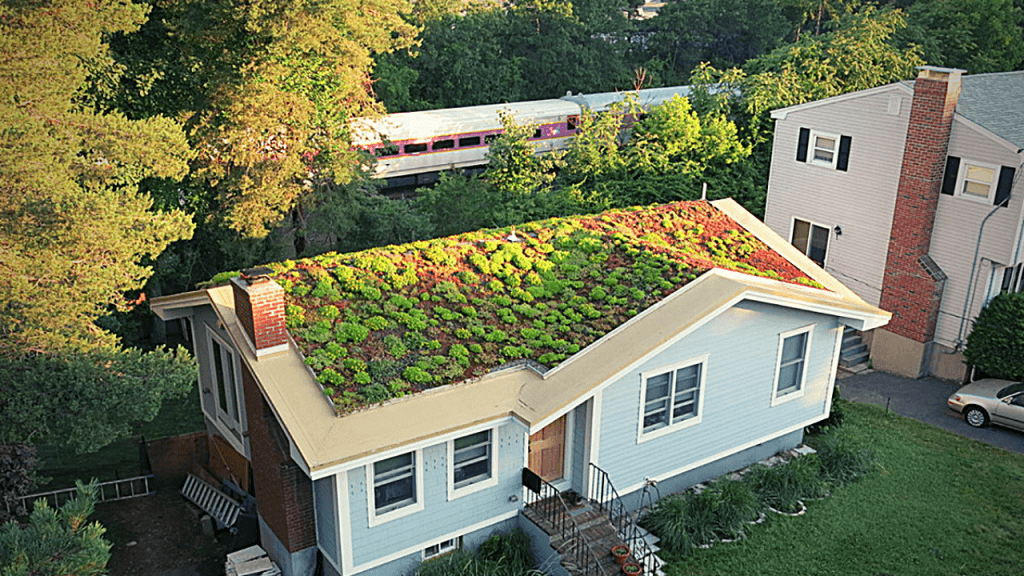
Green roofs are ideal for installation in urban buildings with flat or shallow pit roofs. So what exactly are green roofs? Green Roofs are roofs where you pot bare plants or build an entire garden. These green roofs provide an additional layer of insulation that can bring down the temperature on the roofs. As a result, the need for heating and cooling of the inside space can lower the urban heat island effect.
18. Switch to Solar Power
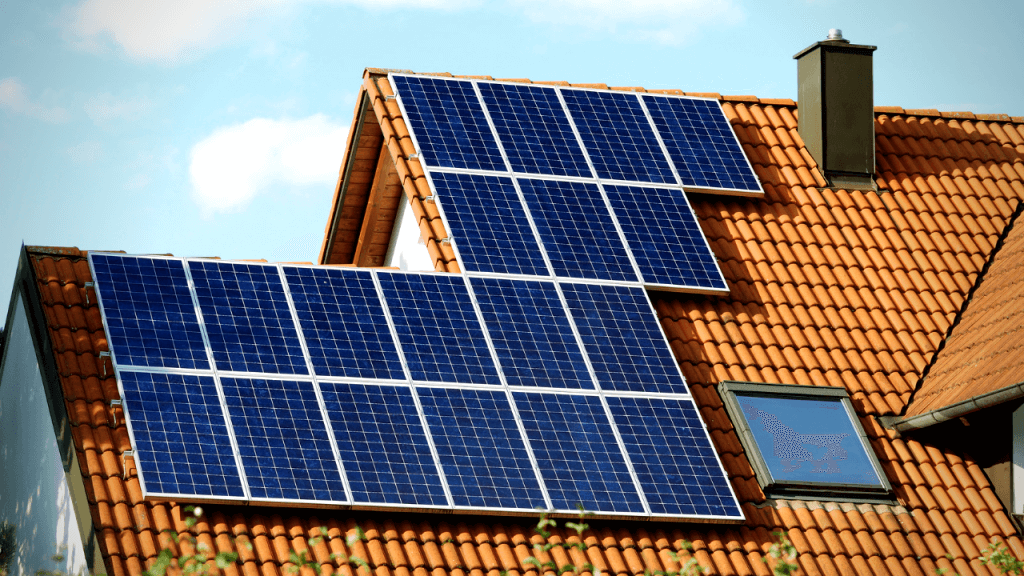
A decade ago, solar was expensive and out of reach for many customers. Today, it’s easy for anyone to acquire if they decide to go that route. Although solar has a high initial cost, it pays for itself in 7-9 years and produces free electricity for the next 15 years. If you decided to go solar, the average cost of electricity would be around two to five cents per kWh over 25 years. [5]
19. Passive Solar Heating and Cooling
Passive Solar Heating and Cooling techniques help homeowners to save money on their utility bills. It is estimated that passive solar heating systems save money–for a home that uses gas can be from $150-$380 per year. It can be environmentally friendly. [6]
Passive solar heating allows homeowners to collect and distribute solar energy through their windows. This is done using materials that hold onto heat during the day and disperse it at night. As a result, homeowners can keep their homes comfortable even in spaces that would get cool. Passive Solar Cooling also reduces your heating costs as well.
Key takeaways: You can try to do many things to get better at conserving energy. A few things like changing your light bulbs from incandescent to CFL or changing your electricity plans will be a quick fix. But to have any long-term effects, you may want to think about switching to solar power from conventional sources (coal, natural gas, etc.). In our next article, check out our guide to the Pros and Cons of going solar.